How to Write an Abstract | Steps & Examples
An abstract is a short summary of a longer work (such as a thesis, dissertation or research paper). The abstract concisely reports the aims and outcomes of your research, so that readers know exactly what your paper is about.
Although the structure may vary slightly depending on your discipline, your abstract should describe the purpose of your work, the methods you’ve used, and the conclusions you’ve drawn.
One common way to structure your abstract is to use the IMRaD structure. This stands for:
Abstracts are usually around 100–300 words, but there’s often a strict word limit, so make sure to check the relevant requirements.
In a dissertation or thesis, include the abstract on a separate page, after the title page and acknowledgements but before the table of contents.
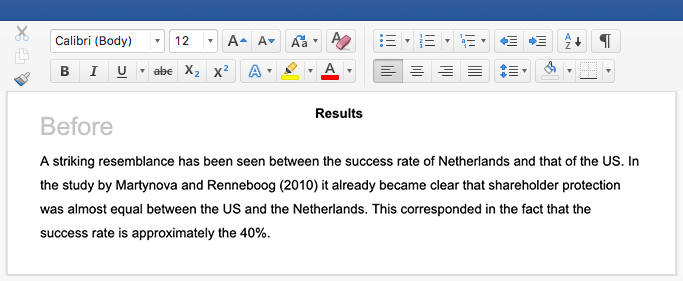
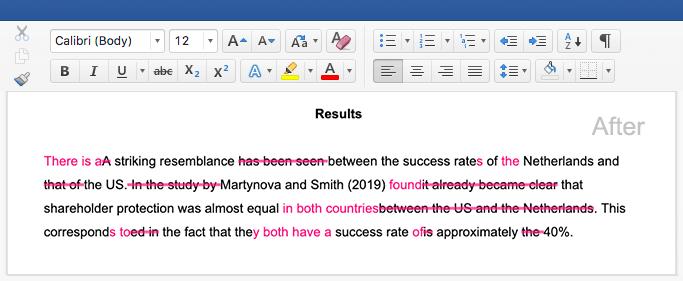
Abstract example
Hover over the different parts of the abstract to see how it is constructed.
This paper examines the role of silent movies as a mode of shared experience in the US during the early twentieth century. At this time, high immigration rates resulted in a significant percentage of non-English-speaking citizens. These immigrants faced numerous economic and social obstacles, including exclusion from public entertainment and modes of discourse (newspapers, theater, radio).
Incorporating evidence from reviews, personal correspondence, and diaries, this study demonstrates that silent films were an affordable and inclusive source of entertainment. It argues for the accessible economic and representational nature of early cinema. These concerns are particularly evident in the low price of admission and in the democratic nature of the actors’ exaggerated gestures, which allowed the plots and action to be easily grasped by a diverse audience despite language barriers.
Keywords: silent movies, immigration, public discourse, entertainment, early cinema, language barriers.
When to write an abstract
You will almost always have to include an abstract when:
- Completing a thesis or dissertation
- Submitting a research paper to an academic journal
- Writing a book or research proposal
- Applying for research grants
It’s easiest to write your abstract last, right before the proofreading stage, because it’s a summary of the work you’ve already done. Your abstract should:
- Be a self-contained text, not an excerpt from your paper
- Be fully understandable on its own
- Reflect the structure of your larger work
Step 1: Introduction
Start by clearly defining the purpose of your research. What practical or theoretical problem does the research respond to, or what research question did you aim to answer?
You can include some brief context on the social or academic relevance of your topic, but don’t go into detailed background information. If your abstract uses specialized terms that would be unfamiliar to the average academic reader or that have various different meanings, give a concise definition.
After identifying the problem, state the objective of your research. Use verbs like “investigate,” “test,” “analyze,” or “evaluate” to describe exactly what you set out to do.
This part of the abstract can be written in the present or past simple tense but should never refer to the future, as the research is already complete.
- This study will investigate the relationship between coffee consumption and productivity.
- This study investigates the relationship between coffee consumption and productivity.
Step 2: Methods
Next, indicate the research methods that you used to answer your question. This part should be a straightforward description of what you did in one or two sentences. It is usually written in the past simple tense, as it refers to completed actions.
- Structured interviews will be conducted with 25 participants.
- Structured interviews were conducted with 25 participants.
Don’t evaluate validity or obstacles here—the goal is not to give an account of the methodology’s strengths and weaknesses, but to give the reader a quick insight into the overall approach and procedures you used.
Step 3: Results
Next, summarize the main research results. This part of the abstract can be in the present or past simple tense.
- Our analysis has shown a strong correlation between coffee consumption and productivity.
- Our analysis shows a strong correlation between coffee consumption and productivity.
- Our analysis showed a strong correlation between coffee consumption and productivity.
Depending on how long and complex your research is, you may not be able to include all results here. Try to highlight only the most important findings that will allow the reader to understand your conclusions.
Step 4: Discussion
Finally, you should discuss the main conclusions of your research: what is your answer to the problem or question? The reader should finish with a clear understanding of the central point that your research has proved or argued. Conclusions are usually written in the present simple tense.
- We concluded that coffee consumption increases productivity.
- We conclude that coffee consumption increases productivity.
If there are important limitations to your research (for example, related to your sample size or methods), you should mention them briefly in the abstract. This allows the reader to accurately assess the credibility and generalizability of your research.
If your aim was to solve a practical problem, your discussion might include recommendations for implementation. If relevant, you can briefly make suggestions for further research.
Keywords
If your paper will be published, you might have to add a list of keywords at the end of the abstract. These keywords should reference the most important elements of the research to help potential readers find your paper during their own literature searches.
Be aware that some publication manuals, such as APA Style, have specific formatting requirements for these keywords.
Tips for writing an abstract
It can be a real challenge to condense your whole work into just a couple of hundred words, but the abstract will be the first (and sometimes only) part that people read, so it’s important to get it right. These strategies can help you get started.
Read other abstracts
The best way to learn the conventions of writing an abstract in your discipline is to read other people’s. You probably already read lots of journal article abstracts while conducting your literature review—try using them as a framework for structure and style.
You can also find lots of dissertation abstract examples in thesis and dissertation databases.
Reverse outline
Not all abstracts will contain precisely the same elements. For longer works, you can write your abstract through a process of reverse outlining.
For each chapter or section, list keywords and draft one to two sentences that summarize the central point or argument. This will give you a framework of your abstract’s structure. Next, revise the sentences to make connections and show how the argument develops.
Write clearly and concisely
A good abstract is short but impactful, so make sure every word counts. Each sentence should clearly communicate one main point.
To keep your abstract or summary short and clear:
- Avoid passive sentences: Passive constructions are often unnecessarily long. You can easily make them shorter and clearer by using the active voice.
- Avoid long sentences: Substitute longer expressions for concise expressions or single words (e.g., “In order to” for “To”).
- Avoid obscure jargon: The abstract should be understandable to readers who are not familiar with your topic.
- Avoid repetition and filler words: Replace nouns with pronouns when possible and eliminate unnecessary words.
- Avoid detailed descriptions: An abstract is not expected to provide detailed definitions, background information, or discussions of other scholars’ work. Instead, include this information in the body of your thesis or paper.
If you’re struggling to edit down to the required length, you can get help from expert editors with Scribbr’s professional proofreading services.
Check your formatting
If you are writing a thesis or dissertation or submitting to a journal, there are often specific formatting requirements for the abstract—make sure to check the guidelines and format your work correctly. For APA research papers you can follow the APA abstract format.
Checklist: Abstract
0 / 8Well done!
You've written a great abstract! Use the other checklists to continue improving your thesis or dissertation.
See all other checklists Return to checklistFrequently asked questions about abstracts
- What is the purpose of an abstract?
-
An abstract is a concise summary of an academic text (such as a journal article or dissertation). It serves two main purposes:
- To help potential readers determine the relevance of your paper for their own research.
- To communicate your key findings to those who don’t have time to read the whole paper.
Abstracts are often indexed along with keywords on academic databases, so they make your work more easily findable. Since the abstract is the first thing any reader sees, it’s important that it clearly and accurately summarizes the contents of your paper.
- How long is a dissertation abstract?
-
An abstract for a thesis or dissertation is usually around 200–300 words. There’s often a strict word limit, so make sure to check your university’s requirements.
- When should I write the abstract?
-
The abstract is the very last thing you write. You should only write it after your research is complete, so that you can accurately summarize the entirety of your thesis, dissertation or research paper.
- Can you cite sources in an abstract?
-
Avoid citing sources in your abstract. There are two reasons for this:
- The abstract should focus on your original research, not on the work of others.
- The abstract should be self-contained and fully understandable without reference to other sources.
There are some circumstances where you might need to mention other sources in an abstract: for example, if your research responds directly to another study or focuses on the work of a single theorist. In general, though, don’t include citations unless absolutely necessary.
- Where does the abstract go in a thesis or dissertation?
-
The abstract appears on its own page in the thesis or dissertation, after the title page and acknowledgements but before the table of contents.
Sources in this article
We strongly encourage students to use sources in their work. You can cite our article (APA Style) or take a deep dive into the articles below.
This Scribbr articleMcCombes, S. (October 13, 2022). How to Write an Abstract | Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved October 20, 2022, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/abstract/